Differences Between Multi-layer Ceramic Technologies, MLCC, LTCC, and HTCC
Multilayer ceramic technology (multilayer ceramic, MLC) is a widely used technology in the modern electronics industry for manufacturing multilayer capacitors and other electronic components. MLCC (multilayer ceramic capacitor), LTCC (low-temperature co-fired ceramic), and HTCC (high-temperature co-fired ceramic) are the three main types of multilayer ceramic technologies, with their differences primarily lying in materials, sintering temperatures, manufacturing processes, and application fields.
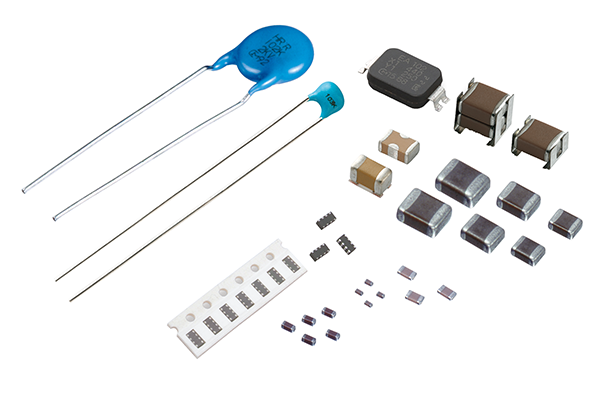
1. Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor (MLCC)
Dielectric Materials: Barium titanate (BaTiO3), titanium dioxide (TiO2), calcium zirconate (CaZrO3), or other dielectric ceramic materials are used.
Metal Materials: Internal electrodes: Nickel (Ni)/Copper (Cu)/Silver (Ag)/Palladium-Silver (Pd/Ag); Terminal electrodes: Copper (Cu), Silver (Ag).
Sintering Temperature: Generally between 1100°C and 1350°C.
Product Type: Capacitor
Application Fields: Widely used in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, communication equipment, etc.
2. Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (LTCC)
Dielectric materials: Glass-ceramics, ceramic-glass composites, and glass-bonded ceramics.
Metallic materials: Low-melting-point metals such as silver (Ag), gold (Au), copper (Cu), and palladium-silver (Pd/Ag).
Sintering temperature: Generally between 800°C and 950°C.
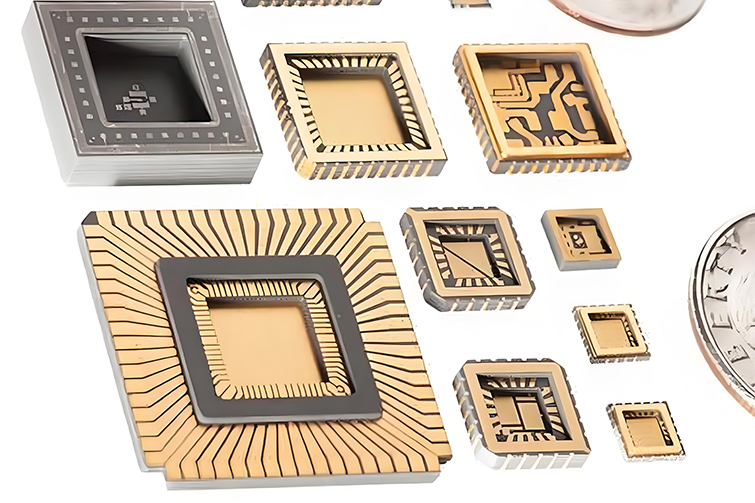
Product types: Filters, duplexers, couplers, baluns, antennas, ceramic substrates, ceramic packaging shells, etc.
Application fields: Primarily used in high-frequency circuits, RF modules, microwave circuits, etc.
3. High-Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (HTCC)
Dielectric Materials: High-temperature ceramic materials such as alumina (Al2O3), aluminum nitride (AlN), or zirconia (ZrO2).
Metal Materials: High-melting-point metals such as tungsten (W), molybdenum (Mo), and manganese (Mn).
Sintering Temperature: Generally between 1600°C and 1800°C.
Product Types: Ceramic substrates, ceramic packaging shells, heating elements, sensors, etc.
Application Fields: Suitable for high-temperature, high-power, and high-frequency applications, such as power electronics, sensors, and aerospace electronic equipment.
The manufacturing processes of MLCC, LTCC, and HTCC are generally similar, with typical multilayer ceramic processes including green tape casting, screen printing, stacking, lamination, cutting, and firing. However, there are significant differences in certain details. For instance, the MLCC process does not require perforation and directly prints the internal electrode paste, whereas LTCC and HTCC perform perforation as needed. Due to the different materials selected for LTCC and HTCC, the sintering process varies in terms of temperature and atmosphere.